| 1. |
In North America, most housing and commercial structures built prior to the 20th century used wood as the major structural material. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 2. |
Recently, there has been less interest in using wood for various types of transportation structures, including bridges. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 3. |
In the latter part of the 20th century, platform framing has dominated the housing market and is widely used in commercial and light industrial applications.
|
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 4. |
Engineered trusses reduce on-site labor and can span greater distances without intermediate support, thus eliminating the need for interior load-carrying partitions. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 5. |
Prefabricated roof trusses are used to form the ceiling and sloped roof of more than two-thirds of current light-frame buildings. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 6. |
Rafters are generally supported on the top plate of the wall and attached to a ridge board at the roof peak. However, because the rafters slope, they tend to push out the tops of the walls. This is prevented by nailing the rafters to the ceiling joists and nailing the ceiling joists to the top wall plates. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 7. |
Log homes nearly always feature wall systems built from natural or manufactured logs rather than from dimension lumber. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 8. |
Mill-type construction has been widely used for warehouse and manufacturing structures, particularly in the eastern United States. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False
|
| 9. |
To be recognized as mill-type construction, the structural elements must meet specific sizes- |
|
|
Columns cannot be less than standard 184 mm (nominal 8 in.) in dimension. |
|
|
Beams and girders cannot be less than standard 140 by 235 mm (nominal 6 by 10 in.) in cross section. |
|
|
All Of the Above |
| 10. |
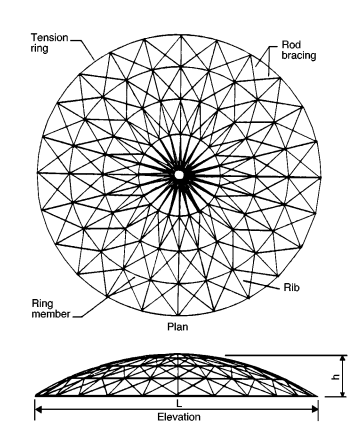
Figure 1.0
What does figure 1.0 illustrate about?
|
|
|
Timber frame structure with typical joint details. |
|
|
Member layout for a radial-rib dome. |
|
|
Pole and post-frame buildings |
|
|
None of the above |
| 11. |
Arch structures are particularly suited to applications in which large, unobstructed areas are needed, such as churches, recreational buildings, and aircraft hangars. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 12. |
Glued laminated timber, commonly referred to as glulam, is an engineered stress-rated product produced by structurally bonding individual lumber laminations. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 13. |
A simple bridge type that has been used for centuries consists of one or more logs used to span the opening. Several logs may be laid side-by-side and fastened together. Which type of bridge is defined here? |
|
|
Log Stringer |
|
|
Sawn Lumber |
| 14. |
Two types of structural composite lumber (SCL)-laminated veneer and oriented strand-are beginning to be used to build timber bridges. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 15. |
Many factors must be considered when designing and constructing wood buildings which includes structural, insulation, moisture, and sound control. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 16. |
The structural design of any building consists of combining the prescribed performance requirements with the anticipated loading. One major performance requirement is that there be an adequate margin of safety between the structures ultimate capacity and the maximum anticipated loading. The probability that the building will ever collapse is minimized using material property information recommended by the material manufacturers along with code-recommended design loads. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 17. |
For most U.S. climates, the exterior envelope of a building needs to be insulated either to keep heat in the building or prevent heat from entering. Wood frame construction is well suited to application of both cavity insulation and surface applied insulation. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 18. |
Wood moisture content levels >20% encourage corrosion of steel fasteners in wood, especially if the wood is treated with preservatives. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 19. |
An important design consideration for residential and office buildings is the control of sound that either enters the structure from outside or is transmitted from one room to another. Wood frame construction can achieve the levels of sound control equal to or greater than more massive construction, such as concrete. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 20. |
Strategies to control moisture accumulation fall into the categories of: |
|
|
Minimize moisture entry into the building envelope |
|
|
Remove moisture from the building envelope. |
|
|
All of the above |
|